
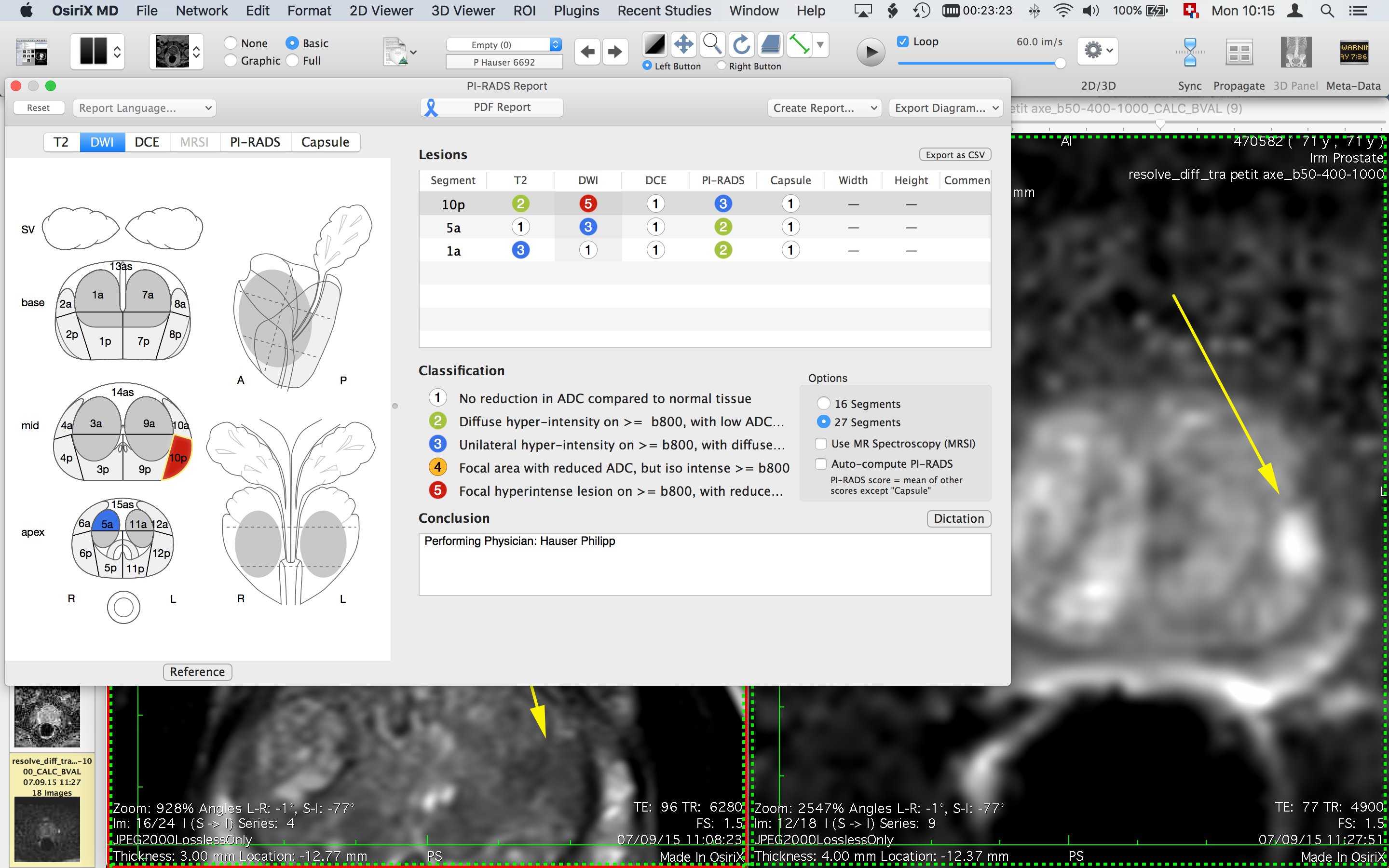
Intracranial arterial calcification (IAC) is commonly seen in major cerebral arteries ( 1– 3) and established as an independent risk factor for stroke ( 4). Compared with the medial IAC, intimal IAC was more often accompanied by eccentric plaques ( p = 0.02), larger plaque burden ( p = 0.001), and IPH ( p = 0.001).Ĭonclusion: Our multimodal imaging-based comparison study on intracranial arteriosclerosis demonstrated that intimal IAC, compared with medial IAC, was more often accompanied by the luminal stenosis, larger plaque burden, eccentricity, and IPH, providing strong evidence for clinical evaluation on the mechanism, risk, and prognosis of ischemic stroke. Intimal calcification was associated with luminal stenosis ( p = 0.003) caused by atherosclerotic lesions. About 79.8% of intimal calcifications and 64.5% of medial calcifications co-existed with atherosclerotic plaques. Results: Among 69 patients with stroke, IAC was identified in 35% of (161/483) artery segments, of which 61.5% were predominantly intimal calcification and 38.5% were predominantly medial calcification. Subsequently, on the vwMRI, we assessed the luminal stenosis, eccentricity, plaque burden, and intraplaque hemorrhage (IPH) as markers of atherosclerosis at each IAC site. IAC was into the intimal or medial pattern. Bilateral intracranial segment of the internal carotid artery, M1 segment of the middle cerebral artery, intracranial segment of the vertebral artery, and the basilar artery were visualized by the multi-detector computed tomography (CT) and vessel-wall magnetic resonance imaging (vwMRI) within 14 days after stroke onset. Methods: Consecutive patients with acute ischemic stroke were included. This study aimed to elucidate the link between the calcification and atherosclerotic disease in the intracranial vasculature.
5Department of Clinical Epidemiology, Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health Boston, Cambridge, MA, United States.

4Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Department of Epidemiology, Erasmus MC University Medical Center, Rotterdam, Netherlands.3Department of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, United States.2Department of Critical Care Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China.1Department of Health Technology and Informatics, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Kowloon, Hong Kong SAR, China.The proposed risk analysis framework has been applied to a vital signs monitoring information system for homecare telemedicine, namely the VITAL-Home System, developed and maintained for a private medical center (Medical Diagnosis and Treatment S.A.).Heng Du 1, Jia Li 2, Wenjie Yang 3, Daniel Bos 4,5, Lu Zheng 6, Lawrence Ka Sing Wong 6, Thomas W. Based on “what–if” studies of system operation, the Bayesian Network model identifies and prioritizes the most critical events. The proposed method exploits the results of the CRAMM-based risk analysis for developing a Bayesian Network model, which presents concisely all the interactions of the undesirable events for the system. Specifically, the CCTA Risk Analysis and Management Methodology (CRAMM) has been utilized for identifying and valuating the assets, threats, and vulnerabilities of the information system, followed by a graphical modeling of their interrelationships using Bayesian Networks. This paper presents a new method for performing a risk analysis study of health information systems. Particularly for safety–critical applications such as the healthcare information systems, which are dealing with human health, risk analysis should be considered a necessity. Often system failures are a result of insufficient planning or equipment malfunction, indicating that it is essential to develop techniques for predicting and addressing a system failure. In a modern technological environment where information systems are characterized by complexity, situations of non-effective operation should be anticipated.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
